7 Hidden Gem Django REST Framework Libraries You Should Know About!
Django REST Framework (DRF) is the go-to tool for building powerful APIs in Django. While DRF provides great built-in features, there are…

Django REST Framework (DRF) is the go-to tool for building powerful APIs in Django. While DRF provides great built-in features, there are several hidden gem libraries that can help you optimize, secure, and supercharge your API development.
Let’s explore 7 must-know DRF libraries that every Django developer should have in their toolkit! 🔥
1. drf-spectacular — Auto-Generate Beautiful API Docs
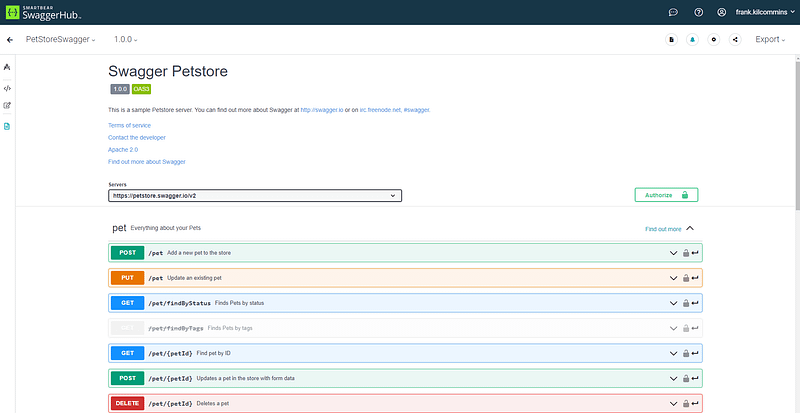
Stop writing API docs manually! drf-spectacular generates fully detailed OpenAPI/Swagger documentation automatically.docs : https://github.com/tfranzel/drf-spectacular
Installation
$ pip install drf-spectacularExample
# settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'drf_spectacular',
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS": "drf_spectacular.openapi.AutoSchema",
}
SPECTACULAR_SETTINGS = {
'TITLE': 'Your Project API',
'DESCRIPTION': 'Your project description',
'VERSION': '1.0.0',
'SERVE_INCLUDE_SCHEMA': False,
}# urls.py
from drf_spectacular.views import SpectacularAPIView, SpectacularRedocView, SpectacularSwaggerView
urlpatterns = [
# YOUR PATTERNS
path('api/schema/', SpectacularAPIView.as_view(), name='schema'),
# Optional UI:
path('api/schema/swagger-ui/', SpectacularSwaggerView.as_view(url_name='schema'), name='swagger-ui'),
path('api/schema/redoc/', SpectacularRedocView.as_view(url_name='schema'), name='redoc'),
]This will generates Swagger, Redoc, and OpenAPI docs. It supports authentication & permissions and fully Customizable with schema extensions.
You can access your API docs at:
- Swagger :
/api/schema/swagger-ui/ - redoc :
/api/schema/redoc/
2. drf-nested-routers — Create Nested API Endpoints
Django REST Framework doesn’t support nested routes by default. This package fixes that by allowing URLs like:
docs : https://github.com/alanjds/drf-nested-routers
Installation
pip install drf-nested-routersExample
The desired URL signatures are:
/domains/ <- Domains list
/domains/{pk}/ <- One domain, from {pk}
/domains/{domain_pk}/nameservers/ <- Nameservers of domain from {domain_pk}
/domains/{domain_pk}/nameservers/{pk} <- Specific nameserver from {pk}, of domain from {domain_pk}How to do it :
# urls.py
from rest_framework_nested import routers
from views import DomainViewSet, NameserverViewSet
router = routers.SimpleRouter()
router.register(r'domains', DomainViewSet)
domains_router = routers.NestedSimpleRouter(router, r'domains', lookup='domain')
domains_router.register(r'nameservers', NameserverViewSet, basename='domain-nameservers')
# 'basename' is optional. Needed only if the same viewset is registered more than once
# Official DRF docs on this option: http://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/routers/
urlpatterns = [
path(r'', include(router.urls)),
path(r'', include(domains_router.urls)),
]3. drf-flex-fields — Optimize API Responses
Instead of returning unnecessary data, let users choose which fields to include or expand in responses.
docs : https://github.com/rsinger86/drf-flex-fields
Installation
pip install drf-flex-fieldsExample
# serializers.py
from rest_flex_fields import FlexFieldsModelSerializer
class StateSerializer(FlexFieldsModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = State
fields = ('id', 'name')
class CountrySerializer(FlexFieldsModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Country
fields = ('id', 'name', 'population', 'states')
expandable_fields = {
'states': (StateSerializer, {'many': True})
}
class PersonSerializer(FlexFieldsModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Person
fields = ('id', 'name', 'country', 'occupation')
expandable_fields = {'country': CountrySerializer}GET /people/142/If the default serialized response is the following:
{
"id": 142,
"name": "Jim Halpert",
"country": 1
}When you do a GET /person/142?expand=country.state, the response will change to:
GET /people/142/?expand=country.states{
"id": 142,
"name": "Jim Halpert",
"country": {
"id": 1,
"name": "United States",
"states": [
{
"id": 23,
"name": "Ohio"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Pennsylvania"
}
]
}
}4. drf-turbo — High-Performance JSON Serialization
Need faster API responses? drf-turbo provides blazing-fast JSON serialization using optimized Python techniques.docs : https://github.com/Mng-dev-ai/drf-turbo
Installation
$ pip install drf-turboExample
import drf_turbo as dt
class UserSerializer(dt.Serializer):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ["id", "name", "email"]This is up to 10x faster than default DRF serializers. It Supports nested relationships and easy drop-in replacement for existing serializers.
5. django-rest-knox — Secure Token Authentication
DRF default token auth isn’t secure enough for production apps. knox provides more secure, time-limited tokens.docs : https://jazzband.github.io/django-rest-knox/installation/
Installation
pip install django-rest-knoxExample
# settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'rest_framework',
'knox',
...
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ('knox.auth.TokenAuthentication',),
...
}python manage.py migrate# views.py
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from knox.auth import TokenAuthentication
class ExampleAPIView(APIView):
authentication_classes = (TokenAuthentication,)
permission_classes = (IsAuthenticated,)
def get(self, request, format=None):
content = {
'foo': 'bar'
}
return Response(content)This Standardized the API responses, supports compound documents and Works with DRF serializers.
6. doser — Handle Authentication
djoser library provides a set of Django Rest Framework views to handle basic actions such as registration, login, logout, password reset and account activation. It works with custom user model.
docs : https://djoser.readthedocs.io/en/latest/introduction.html
Installation
pip install -U djoserExample
# settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'django.contrib.auth',
'rest_framework',
'djoser',
)
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.authentication.TokenAuthentication',
),
}
# urls.py
urlpatterns = [
re_path(r'^auth/', include('djoser.urls')),
re_path(r'^auth/', include('djoser.urls.authtoken')),
]python manage.py migrateRegister a new user:
$ curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8088/auth/users/ --data 'username=djoser&password=alpine12'
{"email": "", "username": "djoser", "id":1}Let’s log in:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8088/auth/token/login/ --data 'username=djoser&password=alpine12'
{"auth_token": "b704c9fc3655635646356ac2950269f352ea1139"}We have just obtained an authorization token that we may use later in order to retrieve specific resources.
Let’s access user’s details by using the authentication token:
$ curl -LX GET http://127.0.0.1:8088/auth/users/me/ -H 'Authorization: Token b704c9fc3655635646356ac2950269f352ea1139'
{"email": "", "username": "djoser", "id": 1}Yay, it works!
Now let’s log out:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8088/auth/token/logout/ --data 'b704c9fc3655635646356ac2950269f352ea1139' -H 'Authorization: Token b704c9fc3655635646356ac2950269f352ea1139'7. drf-jsonapi — JSON API Specification Support
This library formats API responses according to the JSON:API standard.
docs : https://django-rest-framework-json-api.readthedocs.io/en/stable/getting-started.html
Installation
pip install djangorestframework-jsonapi
# for optional package integrations
pip install djangorestframework-jsonapi['django-filter']
pip install djangorestframework-jsonapi['django-polymorphic']
pip install djangorestframework-jsonapi['openapi']Example
# settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'rest_framework',
'rest_framework_json_api',
...
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES": [
"rest_framework_json_api.renderers.JSONRenderer",
],
}Conclusion
These 7 hidden gem DRF libraries will boost your productivity, optimize performance, and simplify API development.
📌 Which library do you plan to use first? Drop a comment below! 🚀




