15 Modern Python Libraries You Must Know in 2025! 🚀
I have discovered these few game changer modern set of libraries that you should must know in 2025.

LEVEL UP YOUR PYTHON SKILLS WITH THESE
15 Modern Python Libraries You Must Know in 2025! 🚀
Hey Everyone, as we know python has a vast set of amazing libraries and many of them are really a game changer.
So, i have discovered these few game changer modern set of libraries that you should must know if you want to stay ahead in 2025.
1. Polars — The Blazing-Fast DataFrame Library
Polars is a blazingly fast DataFrame library written in Rust for manipulating structured data.

Why You Should Use It: This is 10x–100x faster than Pandas. It Supports lazy evaluation for large datasets and works natively with Apache Arrow
Docs : https://docs.pola.rs/
Installation
pip install polarsExample
This is simple example to create a DataFrame using Polars:
import polars as pl
import datetime as dt
df = pl.DataFrame(
{
"name": ["Alice Archer", "Ben Brown", "Chloe Cooper", "Daniel Donovan"],
"birthdate": [
dt.date(1997, 1, 10),
dt.date(1985, 2, 15),
dt.date(1983, 3, 22),
dt.date(1981, 4, 30),
],
"weight": [57.9, 72.5, 53.6, 83.1], # (kg)
"height": [1.56, 1.77, 1.65, 1.75], # (m)
}
)
print(df)shape: (4, 4)
┌────────────────┬────────────┬────────┬────────┐
│ name ┆ birthdate ┆ weight ┆ height │
│ --- ┆ --- ┆ --- ┆ --- │
│ str ┆ date ┆ f64 ┆ f64 │
╞════════════════╪════════════╪════════╪════════╡
│ Alice Archer ┆ 1997-01-10 ┆ 57.9 ┆ 1.56 │
│ Ben Brown ┆ 1985-02-15 ┆ 72.5 ┆ 1.77 │
│ Chloe Cooper ┆ 1983-03-22 ┆ 53.6 ┆ 1.65 │
│ Daniel Donovan ┆ 1981-04-30 ┆ 83.1 ┆ 1.75 │
└────────────────┴────────────┴────────┴────────┘2. Ruff — The Fastest Python formatter & Linter
Ruff is a blazing-fast linter written in Rust, designed to replace Flake8, Black, and isort in one tool.

Why You Should Use It: This is 20x faster than Flake8, supports auto-fixing issues and works as a formatter and linter
Docs : https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/
Installation
pip install ruffExample
We can use uv to initialize a project:
uv init --lib demoThis command creates a Python project with the following structure:
demo
├── README.md
├── pyproject.toml
└── src
└── demo
├── __init__.py
└── py.typedWe’ll then replace the contents of src/demo/__init__.py with the following code:
from typing import Iterable
import os
def sum_even_numbers(numbers: Iterable[int]) -> int:
"""Given an iterable of integers, return the sum of all even numbers in the iterable."""
return sum(
num for num in numbers
if num % 2 == 0
)Next, we’ll add Ruff to our project:
uv add --dev ruffWe can then run the Ruff linter over our project via uv run ruff check:
$ uv run ruff check
src/numbers/__init__.py:3:8: F401 [*] `os` imported but unused
Found 1 error.
[*] 1 fixable with the `--fix` option.we can resolve the issue automatically by running ruff check --fix:
$ uv run ruff check --fix
Found 1 error (1 fixed, 0 remaining).3. PyScript — Run Python in the Browser
PyScript lets you write and execute Python code in the browser, similar to JavaScript.
Why You Should Use It: It enables Python-powered web apps, works directly in HTML and No backend needed!
Docs : https://docs.pyscript.net/2025.2.4/
Installation
We don’t need to install PyScript, instead of this simply add a <script> and link tag, to your HTML document's <head>
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/releases/2025.2.4/core.css">
<!-- This script tag bootstraps PyScript -->
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/releases/2025.2.4/core.js"></script>Example
Create a simple .html file and user <py-script> tag write your python code.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- Recommended meta tags -->
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<!-- PyScript CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://pyscript.net/releases/2025.2.4/core.css">
<!-- This script tag bootstraps PyScript -->
<script type="module" src="https://pyscript.net/releases/2025.2.4/core.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Now you can use <py-script> tag to write your python code inside-->
<py-script>
import sys
from pyscript import display
display(sys.version)
</py-script>
</body>
</html>4. Pandera — Data Validation for Pandas
Pandera helps validate Pandas DataFrames and Series using schema-based validation.

Why You Should Use It: It Catch data errors before processing, works like Pydantic, but for Pandas and supports unit testing for data!
Docs : https://pandera.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
Installation
pip install panderaExample
import pandas as pd
import pandera as pa
# Data to validate
df = pd.DataFrame({
"column1": [1, 4, 0, 10, 9],
"column2": [-1.3, -1.4, -2.9, -10.1, -20.4],
"column3": ["value_1", "value_2", "value_3", "value_2", "value_1"],
})
# Define schema
schema = pa.DataFrameSchema({
"column1": pa.Column(int, checks=pa.Check.le(10)),
"column2": pa.Column(float, checks=pa.Check.lt(-1.2)),
"column3": pa.Column(str, checks=[
pa.Check.str_startswith("value_"),
# define custom checks as functions that take a series as input and
# outputs a boolean or boolean Series
pa.Check(lambda s: s.str.split("_", expand=True).shape[1] == 2)
]),
})
validated_df = schema(df)
print(validated_df)column1 column2 column3
0 1 -1.3 value_1
1 4 -1.4 value_2
2 0 -2.9 value_3
3 10 -10.1 value_2
4 9 -20.4 value_15. Textual — Build TUI Apps in Python
Textual allows you to build modern Terminal UI apps (TUI) in Python with rich components.
Why You Should Use It: To Create beautiful terminal apps, Works with Rich for styling and No frontend experience needed!
Docs : https://textual.textualize.io/tutorial/
Installation
pip install textualExample
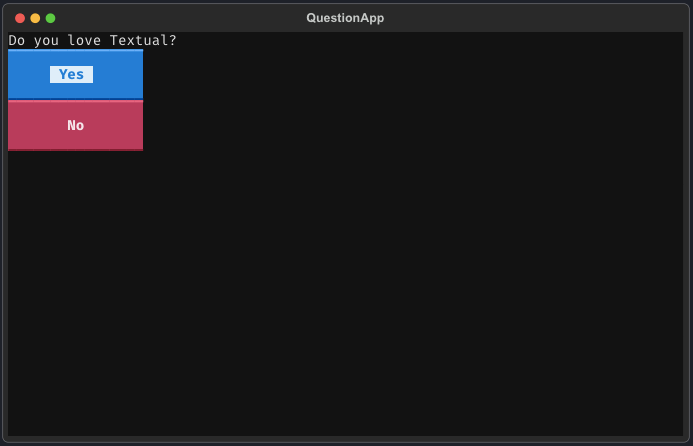
A simple example to create a TUI Apps.
from textual.app import App, ComposeResult
from textual.widgets import Label, Button
class QuestionApp(App[str]):
def compose(self) -> ComposeResult:
yield Label("Do you love Textual?")
yield Button("Yes", id="yes", variant="primary")
yield Button("No", id="no", variant="error")
def on_button_pressed(self, event: Button.Pressed) -> None:
self.exit(event.button.id)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QuestionApp()
reply = app.run()
print(reply)Running this app will give you this result:
6. LlamaIndex — Build Custom AI Assistants
LlamaIndex simplifies indexing and querying large datasets for LLM-powered applications.
Why You Should Use It: It is used for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), Works with OpenAI GPT models and Handles structured and unstructured data.
Docs : https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/#getting-started
Installation
pip install llama-indexExample
Let’s start with a simple example using an agent that can perform basic multiplication by calling a tool. Create a file called starter.py:
- Set an environment variable called
OPENAI_API_KEYwith an OpenAI API key.
import asyncio
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import AgentWorkflow
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
# Define a simple calculator tool
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:
"""Useful for multiplying two numbers."""
return a * b
# Create an agent workflow with our calculator tool
agent = AgentWorkflow.from_tools_or_functions(
[multiply],
llm=OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini"),
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant that can multiply two numbers.",
)
async def main():
# Run the agent
response = await agent.run("What is 1234 * 4567?")
print(str(response))
# Run the agent
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())The result of \( 1234 \times 4567 \) is \( 5,678,678 \).7. Robyn — The Fastest Python Web Framework
Robyn is a high-performance alternative to Flask and FastAPI, optimized for multi-core processing.

Why You Should Use It: It 5x faster than FastAPI. It Supports async and multi-threading and Uses Rust for speed
Docs : https://robyn.tech/documentation/en
Installation
pip install robynExample
Let’s create simple project by using this command :
$ python -m robyn --createThis, would result in the following output.
$ python3 -m robyn --create
? Directory Path: .
? Need Docker? (Y/N) Y
? Please select project type (Mongo/Postgres/Sqlalchemy/Prisma):
❯ No DB
Sqlite
Postgres
MongoDB
SqlAlchemy
PrismaThis will created a new application with the following structure.
├── src
│ ├── app.py
├── DockerfileYou can now write a code in app.py file:
from robyn import Request
@app.get("/")
async def h(request: Request) -> str:
return "Hello, world"You can use this command to run the server :
python -m robyn app.py8. DuckDB — The Lightning-Fast In-Memory Database

DuckDB is an in-memory SQL database that is faster than SQLite for analytics.
Why You Should Use It: It is Blazing-fast for analytics, Works without a server and Easily integrates with Pandas & Polars
Docs : https://duckdb.org/docs/stable/clients/python/overview.html
Installation
pip install duckdb --upgradeExample
A simple example with pandas dataframe :
import duckdb
import pandas as pd
pandas_df = pd.DataFrame({"a": [42]})
duckdb.sql("SELECT * FROM pandas_df")┌───────┐
│ a │
│ int64 │
├───────┤
│ 42 │
└───────┘9. Django — Full-Stack Web Framework

A Django high-level Python web framework for building secure, scalable applications quickly.
Why You Should Use It: It has Built-in ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), Authentication system included, Scalable & Secure and many more
Docs : https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/5.2/
Installation:
pip install djangoExample:
Create a new Django project:
django-admin startproject myproject
cd myproject
python manage.py runserverYou should see you app is running on http:127.0.0.1:8000/
10. FastAPI — High-Performance APIs

FastAPI is a lightweight and fast Python web framework for building RESTful APIs with async support.
Why You Should Use It: Asynchronous support (built-in), Automatic OpenAPI & Swagger UI and Fast (built on Starlette & Pydantic)
Docs : https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/learn/
Installation:
pip install fastapi uvicornExample:
A simple example to create api using FastAPI:
# main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"message": "Hello, FastAPI!"}Run the server:
uvicorn main:app --reloadYou should see you app is running on http:127.0.0.1:8000/
11. LangChain — AI-Powered Applications

LangChain is python framework that simplifies working with LLMs (Large Language Models) like OpenAI’s GPT.
Why You Should Use It: Integrates with OpenAI, Hugging Face, and more, Chain multiple LLM calls together and Supports memory & retrieval-based queries
Docs : https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/
Installation:
pip install langchainExample:
A simple example to create chatbot, using openAI model:
pip install -qU "langchain[openai]"import getpass
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter API key for OpenAI: ")
model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o-mini", model_provider="openai")model.invoke("Hello, world!")You will see a response from chatbot
12. Pydantic — Data Validation & Parsing

Pydantic provides data validation using Python type hints, used in FastAPI.
Why You Should Use It: Automatic data validation, Type hint-based parsing and Works well with FastAPI
Docs : https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/
Installation:
pip install pydanticExample:
from pydantic import BaseModel
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
user = User(name="Aashish Kumar", age=25)
print(user) # User(name='Aashish Kumar', age=25)
print(user.name) # 'Aashish Kumar'
print(user.age) # 2513. Flet — Python for Web, Mobile & Desktop UI

Flet build modern web, desktop, and mobile apps using Python only (no HTML/CSS/JS).
Why You Should Use It: No need for JavaScript or frontend knowledge, Works on Web, Windows, macOS, and Linux and Reactive UI framework
Docs : https://flet.dev/docs/
Installation:
pip install fletExample:
Let’s build a simple Counter App:
import flet
from flet import IconButton, Page, Row, TextField, icons
def main(page: Page):
page.title = "Flet counter example"
page.vertical_alignment = "center"
txt_number = TextField(value="0", text_align="right", width=100)
def minus_click(e):
txt_number.value = str(int(txt_number.value) - 1)
page.update()
def plus_click(e):
txt_number.value = str(int(txt_number.value) + 1)
page.update()
page.add(
Row(
[
IconButton(icons.REMOVE, on_click=minus_click),
txt_number,
IconButton(icons.ADD, on_click=plus_click),
],
alignment="center",
)
)
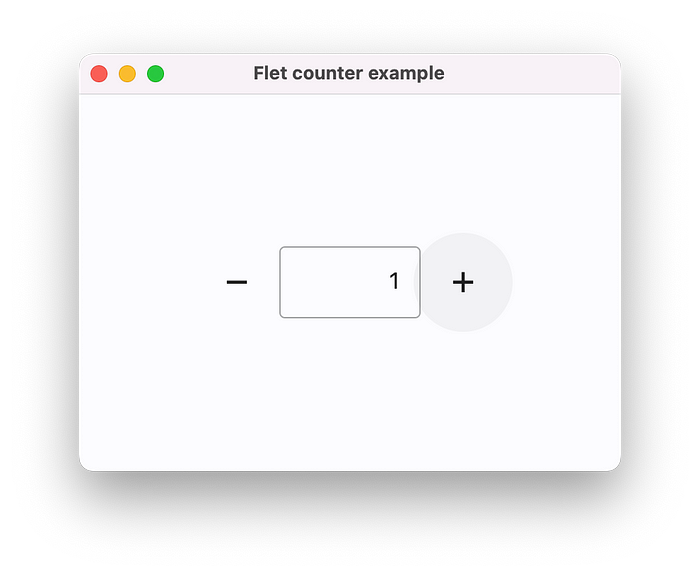
flet.app(target=main)Run the program:
python counter.pyThe app will be started in a native OS window — what a nice alternative to Electron!
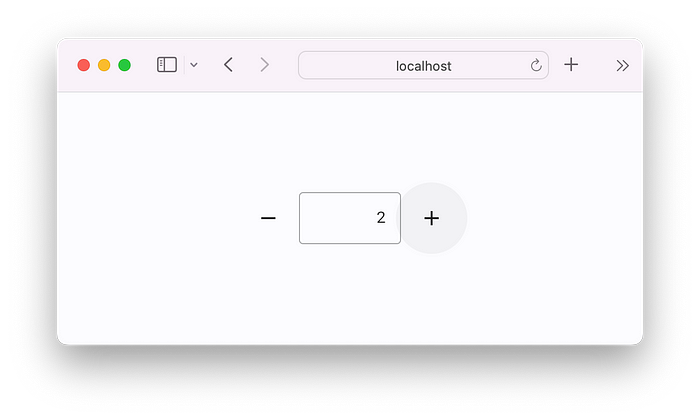
If you want to run the app as a web app, just replace the last line with:
flet.app(target=main, view=flet.AppView.WEB_BROWSER)Run again and now you instantly get a web app:
14. Weaviate — Vector Database for AI & Search

Weaviate is a fast, open-source vector database for semantic search and AI applications.
Why You Should Use It: Ideal for AI-powered search, Stores text, images, and embeddings and Scales for large datasets
Docs : https://weaviate.io/developers/weaviate
Installation:
pip install -U weaviate-clientExample:
To run Weaviate with Docker using default settings, run this command from from your shell:
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50051:50051 cr.weaviate.io/semitechnologies/weaviate:1.29.0Docker instances default to http://localhost:8080To connect to a local instance without authentication :
import weaviate
client = weaviate.connect_to_local()
print(client.is_ready())15. Reflex — Web Apps in Python (Frontend + Backend)

Reflex is a full-stack web framework to build modern web apps in Python, similar to Streamlit but more customizable.
Why You Should Use It: Build React-like UI in Python, State management included and Backend + frontend in one place
Docs : https://reflex.dev/docs/getting-started/introduction/
Installation
pip install reflexExample
You can use these command to create a reflex project:
mkdir my_app_name
cd my_app_name
reflex initCreate a simple app :
# app.py
import reflex as rx
import openai
openai_client = openai.OpenAI()
# Backend code
class State(rx.State):
"""The app state."""
prompt = ""
image_url = ""
processing = False
complete = False
def get_image(self):
"""Get the image from the prompt."""
if self.prompt == "":
return rx.window_alert("Prompt Empty")
self.processing, self.complete = True, False
yield
response = openai_client.images.generate(
prompt=self.prompt, n=1, size="1024x1024"
)
self.image_url = response.data[0].url
self.processing, self.complete = False, True
# Frontend code
def index():
return rx.center(
rx.vstack(
rx.heading("DALL-E", font_size="1.5em"),
rx.input(
placeholder="Enter a prompt..",
on_blur=State.set_prompt,
width="25em",
),
rx.button(
"Generate Image",
on_click=State.get_image,
width="25em",
loading=State.processing
),
rx.cond(
State.complete,
rx.image(src=State.image_url, width="20em"),
),
align="center",
),
width="100%",
height="100vh",
)
# Add state and page to the app.
app = rx.App()
app.add_page(index, title="Reflex:DALL-E")Run development server :
reflex runYou should see your app running at http://localhost:3000.

Final Thoughts
These 15 modern Python tools will help you build faster, smarter, and more scalable applications in 2025.
Which library are you most excited to try? Let me know in the comments!